USB Types and Standards on Computers and Peripheral Devices
The main USB types are USB Type A, USB Type B, and USB Type C and the most common USB standards are USB 2.0, and USB 3.0. What are their main differences? How is each suited for different usage environments?
Introduction
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a hardware that enables serial connections of peripheral devices to computer motherboards. While computers have internal components such as CPUs, RAM, Fans, and more, external components are also needed to increase operability and functionalities. Whereas there are various types of ports for external devices, the USB port is one of the most common and widely used ports on a computer. We can be sure that you have used the USB port of your computer at least once in the past week.
Since the start of the twentieth century, many peripherals devices have been designed and configured to use the common USB port to connect to computers. Some devices are directly fitted with connectors that are plugged into USB ports to function. Further, other devices such as cameras required compatible cables to connect them to a computer’s USB port. Peripheral devices that are often connected through the USB port are;
Wired Mice
Wired Keyboards
Network Adapters (USB Network Interface Cards [NIC])
Video Game controllers
Mobile phones
Tablets
Printers
Scanners
Digital Cameras
External Hard Disk Drives
Flash Disk Drives
USB-powered Computer Speakers
External Computer Cameras
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a technology that is developed for communication (transfer of data) and power supply between peripheral devices and computers.
Although USB cables are classified as just that, USB cables, it is imperative to note that they have evolved over the years in terms of shape, size, and connector types, which has affected fundamental features such as speed and reliability over long distances. You can easily identify the type of each USB cable by simply looking at it. Therefore, let's first briefly, but comprehensively, explore the different types of USB types and standards and their basic features.
Difference between USB Type and USB Standard
USB Type is determined by its physical appearance while USB standard is determined by the supported data transfer speed and the power transfer rate.
USB Types
1. USB-A (USB Type A)
Available since 1996, this is the first and still the most common USB form factor. USB Type A ( USB-A) is rectangularly-shaped and found in devices, including computers, gaming consoles, and TVs.
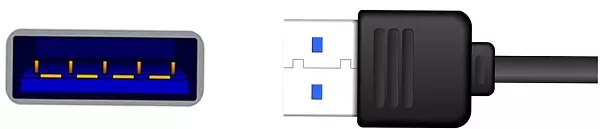
Most cables today have a USB-A connector on one end, and another type (such as USB-B) on the other end.
These cables come in either USB 1.0, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or USB 3.1 standards.
2. USB-B (USB Type B)
USB Type B cables are also referred to as USB printer cables as they are commonly used to connect larger devices such as printers and scanners to computers. Further, you can find these USB B ports on computer monitors as they are also used to expand the functionalities of the monitors.

Most USB-B cables have a USB-A configuration on the other end, which is used to connect to a USB-A port on a computer or laptop. However, newer USB-B cables have moved to new other-end configurations including USB-C; hence they are USB-B to USB-C cables.
These cables come in either USB 1.0, USB 2.0, or USB 3.0 USB standards.
3. USB-C (USB Type C)
USB C cables are the current cables tasked with high-speed data transfers and powering and charging high-powered devices. USB C ports are used in most modern devices including smartphones, gaming controls, wireless headphones and earphones, microphones, and more.
Further, modern laptops and desktops have USB-C ports and therefore can be connected using USB-C to USB-C cables. However, Most USB C cables have a USB A connector on the other end.

Image Credit: Hp
These cables come in either USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, or the new USB4 USB standards.
One major difference between USB C and other USB-type cables is that it is reversible; that is, a USB C connector can be plugged into a USB C port either way. So often, we have to make two or more tries to plug a USB Type-A plug into a USB Type-A receptacle.
USB Type C is gaining popularity as more and more devices are fitted with the Type C port. Whereas their popularity is currently attributed to manufacturers’ choices, there are policies in place to encourage their use. In October 2022, the European Union (EU) put across legislation that is aimed at standardizing all mobile charges. The law, set to be applied by December 2024, requires all rechargeable-via-cable devices coming into the EU to be fitted with a Type-C port for charging purposes, regardless of the manufacturer. These devices include mobile phones, gaming consoles, chargeable speakers, mice, and keyboards. This law is aimed at reducing electronic waste (e-waste).
4. Mini USB Cables
Both Type-A and Type-B cables have smaller versions, referred to as Mini-A and Mini-B respectively. Their small size allows them to be used in smaller devices, including portable cameras, mobile phones, and small gaming controls.
These cables come in either USB 1.1 or USB 2.0 USB standards.
5. Micro USB
Micro USB is a cable that is too familiar to most of us, especially if you own an android smartphone. Even if you have never known it by name, we know this connector looks familiar.

The Micro USB port is found in android smartphones, gaming controllers, rechargeable mice and keyboards, rechargeable speakers, and others.
A Micro USB cable is used for both data transfer and device charging. Commonly, Micro USB cables are fitted with a Type-A connector on one end of the cable.
These cables come in either USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or USB 3.1 USB standards
USB Standards
While physical characteristics are used to determine the types of USB cables, they are also characterized by their standards, which have evolved over the years. Below, we explore the different types of USB Standards which are USB 1.0, USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and USB 4. Below, we have discussed the common USB standards.
1. USB 1.0 Standard
The first USB-A cable was the USB 1.0. As with any other first technological device, the first USB 1.0 Type A cable was prone to timing and power limitations for longer cables. The USB 1.0 Type A cables have a data transfer speed of 1.56 Mbps (Megabits per Second or Mbits/S) and a power transfer of 100mA. The USB 1.0 standard receptacle has a white ridge.
USB Type A and USB Type B have the USB 1.0 Standard.
2. USB 1.1 Standard
The limitations of USB 1.0 prompted the release of USB 1.1 in 1998. The highly noticeable upgrade was the data transfer speed of 12 Mbps (Mbits/S).
USB Type A, USB Type B, and their Mini types of connectors have the USB 1.1 Standard.
3. USB 2.0 Standard
The USB-A 2.0 Standard was introduced in 2001 and supported up to 480 Mbps (Mbits/S). The USB 2.0 standard receptacle has a black ridge.
All USB types, including Type A, Type B, and Type C, all Mini and micro connectors have a USB 2.0 variant making it the most common of all USB standards.
4. USB 3.0 Standard
This standard was released in 2008. It is imperative to note that the USB 3.0 standard introduced the SuperSpeed (SS) type, which supports up to 5 Gbps (Gigabits per second). Modern computers have the USB 3.0 specification emphasized in the specs section. The reason for this emphasis is because of the superfast transfer speed offered by the USB 3.0 standard. Further, the USB 3.0 has a power transfer rate of up to 900mA.
The USB 3.0 standard is available in Type A, Type B, Type C, Micro-A, Micro-B, and Micro-AB USB connectors.

It is possible to determine if a USB Type A or USB Type B connector has a USB 3.0 standard since they usually have a blue ridge in the connector, as opposed to the usual black or white ones.

However, this is not to say that every blue-ridged USB port supports the USB 3.0 standard as the computer’s motherboard must have the capability to process the high transfer speeds.
The SuperSpeed (SS) type is also extended to the Micro USB, including Micro-A, Micro-B, and Micro-AB connectors.
The USB 3.0 standard is backward compatible with USB 2.0. Further, 3.0 USB standard A and B connectors have the same pin configuration as the 2.0 standard A and B connectors; however, the USB 3.0 standard A and B connectors have additional pins to support SuperSpeed (SS).
Observe the Micro-B connector below. If you have connected an external hard disk drive to a computer, chances are you have used a cable with the connector below.
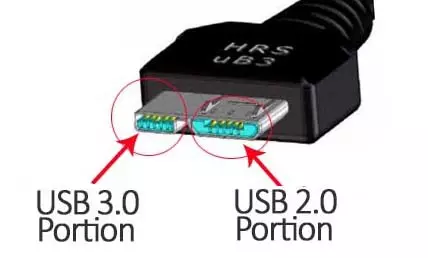
The above Micro-B cable has both the 2.0 portion and the USB 3.0 option. therefore you can use a Micro-B connector to plug in both the 3.0 and 2.0 standards or android's Micro USB (see above) to connect to the 2.0 portion. Both types will work, however, the double-portioned connector will support higher transfers that the single 2.0 portion connector.
5. USB 3.1 Standard
Released in 2013, the USB 3.1 standard introduced the USB SuperSpeed+ (SS+) type which featured a data transfer speed of 10 Gbps (Gigabits per second). The 3.1 USB standard also has a power transfer rate of up to 1.5A.
The USB 3.1 standard is available in Type A, Type B, Type C, Micro-A, Micro-B, and Micro-AB USB connectors.
6. USB 3.2 Standard
Introduced in 2017, the USB 3.2 standard has a data transfer speed of 20 Gbps and a power transfer rate of up to 5A.
The USB 3.2 standard is available in Type C USB connectors.
7. USB4 Standard
The USB4 standard was introduced in 2019 and has a data transfer speed of 40 Gbps, and a power transfer rate of up to 5A. Developed by {Intel Corp}, the USB4 standard is based on Thunderbolt technology and allows high-speed power, data, and video signals over a single connection.
The USB4 standard has backward compatibility with USB 3.2, USB 2.0, and Intel’s Thunderbolt 3.






