CPU Clock Speed, Overclocking, and CPU Cores Explained
What is CPU Overclocking? Ho do I overclock a CPU? How does clock speed and number of cores affect performance? Difference between processor base frequency and max turbo frequency.
CPU Clock Speed
When buying a new computer, there are a few things you probably notice: the size of the Hard disk or SSD, the size of RAM, display ports, and the processor type and rating. Processor type and other fundamental processor specifications are written in a single line as:
Intel Core i7-4790S Processor @ 4.00 GHz
For this specific processor, the clock speed is 4.00 GHz.
A CPU's clock speed is best described as the number of cycles executed per second and is often measured in a frequency's SI unit Hertz (Hz). Modern CPUs have their frequencies represented in gigahertz (GHz). Therefore, the CPU described above does 4 billion cycles every second. Different CPUs have different speeds, but generally modern CPUs can rate anywhere between 1.5 GHz to more than 6 GHz.
CPU Cores
Since we know what a CPU's clock speed is, let's look at a critical specification of the CPU - the CPU cores. While a CPU is a single chip, a core is an independent processor inside the chip - think of it as a CPU inside a CPU. A core is responsible for processing data to complete a task. If a CPU has a single core, the core would take data, process it as needed, and store it before moving to the next set of data.
As applications became intensive, the concept of multi-core arose. Multicore is the presence of more than one processor in a single CPU chip - or in our case, CPUs with a CPU. If each core operates independently and uses a serial approach to process data, then the more cores a computer has, the more data it can simultaneously process. Modern computers require multiple-core CPUs due to the high number of processes running either running in the background or started by a user.
Initially, CPUs were single-core, then came dual-core (2 Cores). Today, there are quad-cores (4 cores) and some CPU processors with even up to 24 cores. For instance, the Intel Core i7-4790S Processor @ 4.00 GHz has 4 cores.
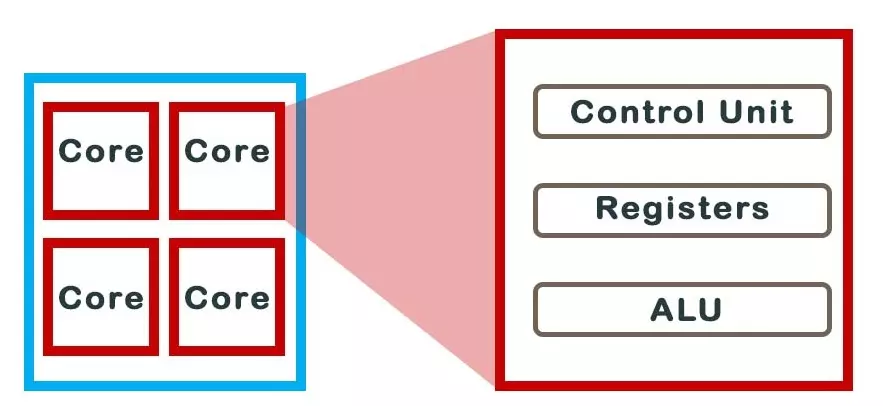
The image above shows a 4-core processor with the corresponding infrastructure, including control unit, registers, ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit).
Clock Speed and CPU Cores in Performance
Both clock speed and the number of cores are critical specifications of a CPU chip. When a CPU has an X number of cores and a clock speed of, say, n GHz, each of the X cores has n GHz speed.
For the Intel Core i7-4790S Processor @ 4.00 GHz CPU, each of the 4 cores has a 4.0 GHz speed. Therefore, each of the 4 cores has a speed of 4.0 GHz and NOT 1 GHz (4 GHz / 4 Cores = 1)
When CPUs had a single core, the higher the frequency of the CPU the higher the volume it could process in a given time. Therefore a single core 2.4 GHz had better performance than a single core 1.8 GHz. When this concept is extended to modern CPUs, one could say that a 4.0 GHz CPU can perform better than a 3.5 GHz CPU. Whereas this is expected, it is not always the case in modern CPUs due to their sophisticated design and architecture.
Therefore, when comparing two similar CPUs, it is best to interrogate all specifications such as Base frequency, Max Turbo Frequency, Bus Speed, Thermal Design Power (TDP), supported memory types, processor graphics, security, and more.
Processor Base Frequency vs Max Turbo Frequency
A CPU frequency is given in two variants - processor base frequency and max turbo frequency.
For instance, the Intel Core i7 4790S processor has a specification of 3.20 GHz base frequency and 4.0 GHz max turbo frequency. Further, the Intel Core i9-10850K processor has a base frequency of 3.60 GHz and a max turbo frequency of 5.20 GHz.
A processor's base frequency is its maximum clock speed when working under normal conditions (light loads). On the other hand, a processor's max turbo frequency is the highest clock speed that a CPU can reach under the maximum workload possible
A CPU operating at the base frequency usually has a set thermal design power (TDP) level that should not be exceeded. However, when operating Max turbo frequency, the CPU draws more resources, particularly power, which ultimately increases the temperature being generated by the CPU. Under base frequency operations, the Intel Core i7 4790s processor has a TDP of 65 W (Watts) while the Intel Core i9-10850K processor has a TDP of 125 W. Some processors can have a higher TDP ratings for their Max Turbo Frequency settings.
Adjusting Between Base Frequency and Max Turbo Frequency
Today's CPUs are dynamic processors, meaning that they automatically adjust their clock speeds depending on the workload and the set thermal upper limit (the highest TDP supported by a processor).
Intel's Turbo Boost Technology manages the adjustment of processors' clock speeds while maintaining them well within the specified safe temperature and power limits. Intel notes that a processor with Turbo Boost Technology capability has the feature already enabled by default and no further installation or configuration is required from the user. However, users can disable the feature in the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) section of their computers; however, this action is not recommended.
Intel's turbo boost technology 2.0 is available in most Intel core processors newer than the 2nd Generation, including Intel Core i5, i7, i9, and Intel Xeon processors. Intel has a 3.0 turbo boost technology available for more advanced CPU processors. One major upgrade on the 3.0 turbo boost is its capability to boost the clock speed of each individual core, and direct workload to the boosted CPU cores.
Overclocking a CPU: Manually Increasing the Clock Speed
It is possible to manually increase the clock speed of your computer's CPU in search of higher clock speeds and possibly better performance. Simply put, overclocking aims to increase a CPU's clock speed above its baseline frequency; say from 3.0GHz to 3.5Ghz. An overclocked processor can operate at higher clock levels than the specified max turbo frequency.
Overclocking a CPU processor is guaranteed to give you better hardware performance without spending extra. If you are a gamer or you simply want to get better CPU performance, overclocking is the route to take.
However, before manually increasing a CPU's clock speed, it's imperative to put a few things into consideration:
1. CPU is Unlocked for Overclocking
First, ensure that your CPU has overclocking features. For instance, Intel specifies both the K-series and the X-series as having overclocking features. You can know if your processor is the K or X series by checking the processor name and number. For instance, Intel Core i9-12900K Processor within the K-series can be overclocked since the K denotes the processor has been unlocked.
2. Motherboard allows Overclocking
Overclocking a CPU requires additional resources such as voltage, memory buses, and more. Therefore, your motherboard should be able to support the additional requirements as put forth by the processor. You can check your computer's motherboard model number against motherboards that have overclocking capabilities.
3. Additional Cooling System
Overclocking means higher voltages and hence higher temperatures. Each processor has a set maximum temperature that shouldn't be exceeded either at the base frequency or max turbo frequency. Once you overclock a CPU, you should be aware that the increase in voltage consumption by the CPU will increase the temperatures dissipated by the processor. Therefore, your factory cooling system most likely will not work. You will need to have a custom cooling system for your CPU; either air-cooled or water-cooled.
4. Gradual Clock Speed Increments
Remember to overclock your processor in small steps and keep track of all your numbers - there will be many. Gradually increase the clock speeds on all CPU cores while continuously checking the system for stability. Compare each increment against benchmark values more so for processor voltage and temperature.
5. Documentation
Most of all, document the changes you make. In case the system fails, you can easily revert to the default settings or the last stable clock speeds.






