IPv4 Address - What is IPv4 Address? IPv4 Examples
What is an IPv4 Address?
This is the older and most common version of IP addresses.
An IPv4 address has four parts each consisting of 8-bit binary numbers that start from 0 to 255. The four different groups of numbers are separated by a decimal (dot/point).
An example of an IP address is 81.214.149.9
One of the fundamental characteristics of an IP address in any network is uniqueness. IPv4 addresses are 32 - bit and can therefore have 232 combinations. Therefore, there are 4.3 billion possible combinations of IPv4 addresses.
However, there is a problem. As of 2022, there were 14.4 billion device internet devices (IoT) connected worldwide. This number is even less than the world population (about 7.837 billion as of 2021)/ With a limit of 4.3 billion unique IP addresses, a solution is needed to assign unique addresses to these devices.
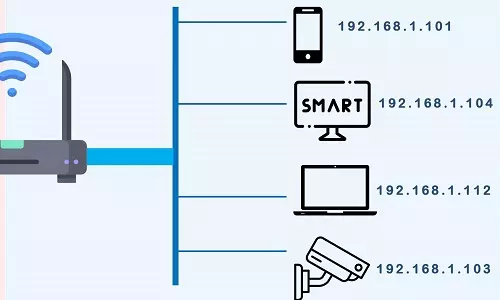
1. Use of Network Address Translation (NAT)
One was to develop a technology that can group devices under the same public router. Network Address Translation was developed so that devices connected to the internet through routers could be assigned private IP addresses by the router. Therefore 1 router with a single public IPv4 address could assign private addresses to 100 internet devices connected to it instead of all 100 devices having unique IPv4 addresses. This system formed the private networks.
2. IPv4 vs IPv6
The other technology that emerged to mitigate the fast consumption of the 4.3 billion unique IPv4 addresses was the development of a second IP version. A new IPv6 addressing system emerged and was launched in June 2012. IPv6 addressing systems have 2128 unique combinations. This means there are 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 possible unique IPv6 combinations. Now that's enough addresses to last us several years, if not decades.