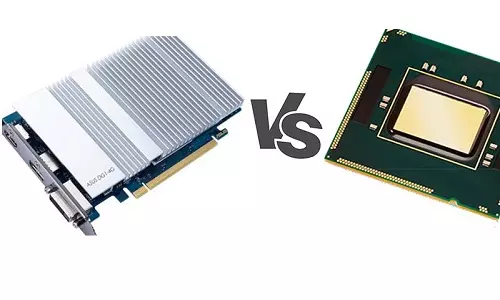
Discrete Graphics Card (GPU) - Simply Explained
What is a discrete graphics card? Differences between a discrete graphics card and an integrated graphics card. Choosing between a discrete and an integrated graphics card.

A GPU (Graphical Processing Unit) is a fundamental component in laptops and PCs, particularly if you are into gaming, or use heavy video applications such as video editors and other graphics-intensive applications such as simulators.
When purchasing a PC or laptop, you might (or might not) be interested in a computer with high graphics processing power. By default, we all want a computer that exceeds what it will be used for, hence the nudge to get a computer with a high graphics processing performance. Not all PCs or laptops have graphics cards; however, those with graphics cards can have either the discrete graphics card or the integrated graphics card.
In computing, you cannot discuss a graphics card and not mention the CPU(Central Processing Unit) due to their similarities and functionalities.
Discrete Graphics Card
In English, the term discrete means individually separate. Just as the name suggests, a discrete graphics card means a GPU that exists separately from the CPU on the motherboard. A discrete graphics card comes with its memory called VRAM (Video Random Access Memory).
Essentially, a discrete graphics card handles all the video rendering tasks and uses the VRAM to store graphical processing information. The VRAM is a special type of memory and is similar to a computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory); however, the VRAM is much faster and can store large amounts of information compared to the RAM. Remember the statement that a GPU and CPU are similar? While the discrete graphics card uses VRAM for temporary data storage, the CPU uses - you guessed it - RAM, for the same purpose; temporary data storage.
There are two ways discrete graphics cards can exist on a motherboard - either placed directly on the motherboard or connected through a special port on the motherboard known as a PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) port. The latter is the case with most desktop PCs while the former is the case with laptops.
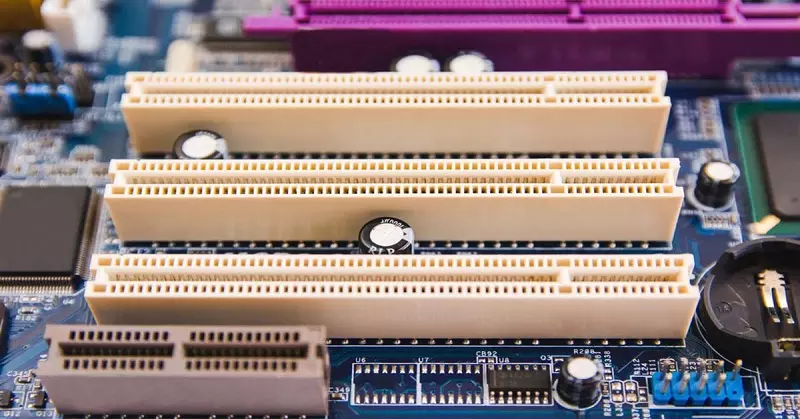
PCIe Slots (Sockets) on a Desktop PC Motherboard
Discrete graphics cards have their cooling system due to the immense heat that they generate.
In laptops, a GPU chip will have part of the heat sink contacting it and a fan connected to the heat sink. In high-end laptops, the GPU heat sink will be separate from the CPU heat sink, and dedicated fans will be installed near the chip. Further, heat vents are placed directly opposite the GPU chips on the laptop casing.
In desktops where most discrete graphics cards are connected through the PCIe slot, the Graphic Cards have fans attached to them. A discrete PCIe graphics card can have two or three fans tasked with cooling the graphics card. The discrete graphics card's improved cooling system helps keep it in optimal performance and increases its lifespan.
Discrete graphics cards require more power to run than integrated graphics cards. Due to the additional electric circulatory components, including the GPU chip itself and VRAM, discrete graphics cards will pull more power from the power supply than integrated graphics cards. The increased consumption of power is greatly attributed to the significant amount of heat generated.
Discrete graphics cards exist as separate hardware on a computer which adds to the weight and bulkiness of the computer. Whether placed directly on the motherboard, for laptops or inserted in a PCIe slot, for desktops, discrete graphics cards add to the complexity of a laptop's design and increase a computer's fault’s surface area.
Integrated Graphics Card
Just as the name suggests, integrated graphics cards are built into a computer’s main processor, CPU. Simply put, the graphics card and CPU are within the same chip. Also known as shared graphics, integrated graphics cards lack independent hardware and rely on a CPU’s RAM and processing power to undertake its graphical processes. Integrated graphics cards have a small footprint on a laptop’s or PC’s motherboard which greatly reduces a fault’s surface area.
The inbuilt design of integrated graphics cards enables them to consume much less power than discrete graphics, which results in significantly less heat created. For laptops and small form factor (SFF) systems, integrated graphics help prolong a battery’s life as there is no demand for much power from the unit. Further, there is no need for complex cooling systems on the motherboard as a common, smaller heat sink, and a fan is enough since less heat is generated by integrated graphics cards.
An integrated graphics card does not have independent memory as the discrete graphics card as the latter has VRAM. Integrated graphics cards rely on RAM to temporarily store graphical information, thereby occupying a percentage of a system’s RAM storage. For instance, if a computer has 6GB of RAM and integrated memory with a shared memory of 2GB, the integrated graphics card will reserve the 2GB as video graphics leaving the CPU with 4GB of RAM. When a demand for more RAM is made by the graphics card from processes that are graphically demanding such as video editing, a user is likely to experience slowed processing, freezing, or even a system crash.
The architecture of an integrated graphics card makes it weaker compared to a discrete graphics card. However, this makes laptops and PCs with integrated graphics cards cheaper than those with discrete graphics.
Discrete graphics card vs Integrated graphics card - What should I get?

NVIDIA Integrated Graphics Card and a Discrete Graphics Card
The differences between discrete graphics and integrated graphics come down to performance and processing power. Therefore, before weighing in on what you most prefer, it's best to consider the workload that your laptop or PC will process. If you are to use the computer for lightweight tasks such as browsing, creating and processing documents, or light gaming, then a laptop or PC with integrated graphics will be enough. Furthermore, integrated graphics cards have become more advanced in recent years thereby improving their performance.
However, discrete graphics cards have equally been advanced which has improved their processing power and performance making them more suitable in some environments than integrated graphics cards . Let’s explore tasks that require discrete graphics other than integrated graphics.
Graphic-intensive games, particularly those among the latest trends, require Discrete graphics with independent memory (VRAM) and cooling systems to keep up with the high graphic renders required by the games.
Video production and editing, illustrations, and animations that are heavily reliant on the graphic properties of a system more so when rendering high-resolution videos and 3D animations.
Game design and development and graphic design using resource-demanding applications such as the adobe bundle and others that support both 2D and 3D.
In some settings, an integrated graphics card might work; however, as the user, you should expect poor performance and system malfunctioning. It is best to check your graphics against an application's graphics requirements. For instance, according to the EA, the Need for Speed Unbound, a 2022 game requires AMD’s RX 570 or Nvidia’s GTX 1050 Ti as the minimum requirements. AMD's RX 570 has a base frequency of 1168MHz, a board power requirement of 150W, and a memory size of 8GB.
Discrete Graphics Card vs Integrated Graphics Card: In Summary
Before buying a laptop or PC, here is a summary of what to consider when it comes to discrete graphics cards vs integrated graphics cards.
The advanced features offered by discrete graphics make computers with discrete graphics cards expensive in terms of cost compared to those with integrated graphics. If you choose to upgrade your graphics card at a later date, you can get a desktop PC with an empty PCIe slot where a new graphics card can be installed.
Discrete graphics cards generate significant amounts of heat compared to integrated graphics cards. Therefore, ensure the operating environment is cool. If you are going for a desktop PC and looking for better cooling, you can install a custom water or air PC cooling system, more so if you are building a PC.
Before buying a laptop or PC, evaluate what the computer will be used for. Buying a computer with discrete graphics cards and using it to browse the internet and perform light jobs such as writing a document can be considered overkill. Remember that a graphics card only handles graphical processes; therefore if your tasks do not involve graphics, an integrated graphics card is the way to go. Further, as we have discussed above, a PC with integrated graphics card and being used for graphic-intensive applications and processes such as animations will often perform poorly, freeze, or even shut down.
Discrete graphics cards consume more power compared to integrated graphics cards . Therefore, especially on a laptop, the battery will drain faster if it has a discrete graphics card compared to one with an integrated graphics card, which might shorten the lifetime of the battery. To solve the battery charge issue, get a laptop whose power charge rating is about 7000 mAh. A battery is designed for a specific board due to voltage and amp variances; therefore, one cannot simply upgrade to a battery with a high capacity, although technically, you can. Before taking such a step, it is recommended that you consult your device’s manufacturer or talk to a technician near you. The safest way is to purchase a laptop power bank especially if you do not always have access to an AC charging port.
When going for an integrated graphics card computer, it is recommended to upgrade your RAM size, especially if you feel that your system is becoming slower overtime, freezing, or even crashing.
Summary of Discrete Graphics Card vs Integrated Graphics Card
| Discrete Graphics Card | Integrated Graphics Card |
|---|---|
| Is separate from the CPU | Is inbuilt into the CPU |
| Use VRAM as memory | Use RAM as memory |
| Produces significant amount of heat | Produces significantly less amount of heat |
| Consumes more power | Consumes less power |
| Has a high graphic and rendering performance than integrated graphics card | Has a low graphic and rendering performance compared to discrete graphics card |
| Commonly found in desktop PCs. Some laptops and small form factors(SFF) can also have discrete graphics cards. | Commonly found in laptops and small form factors(SFF). |