Parts of a Computer System and their Functions - Internal and External Parts
Monitor, Keyboard, and mouse are the most common external parts of a computer. Computer Motherboard, CPU, GPU, and RAM are the common internal parts of a computer
A computer is a machine tasked with running complex sets of instructions. A computer can be used to perform simple tasks such as addition of simple numbers such as 1 + 1 to drawing a picture to sending spaceships into space and controlling satellites thousands of miles (and kilometers) from the earth's surface.
The complexity of a computer has increased overtime as new technologies emerge including storage and electrical engineering and design. Although this introduction draws a computer as a complex system, its building blocks are easy to understand. Doubt how easy it is? Consider a computer as a music band. You can identify the different instruments played and even recognize the sound made by each instrument.. It is that simple.
However, in this article, we shall not explore how each musical instrument is built, its features, or how sound is produced. We can only focus on the music. Lets see the main components (the music instruments) of a computer.
Computer components can either be internal or external.
External Parts
Computer Case
A computer case is a box that houses all other components, including the motherboard, fans, hard drives, optical drivers, and more. A computer casing can have different components including buttons, cut-out holes for the various ports and lights, and ventilation fins on the front, back, or sides. The casing can be made of plastic or metal.

Computer casings come in various sizes depending on the functionalities provided. Further, the design of the computer case can determine if the computer is a desktop or tower.
A laptop casing is smaller than a desktop case. This is because a laptop has less and smaller components than a desktop. Compare a laptop fan to the desktop fan below. Notice the difference.
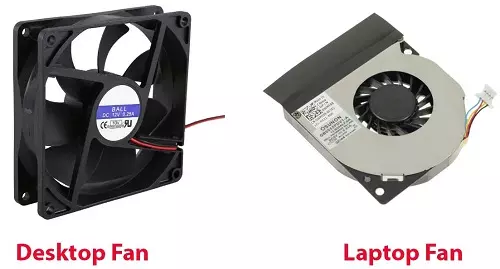
You can see the reason why desktops are larger than laptop computers.
Computer Monitor
If you are reading this desktop computer, you can see it through a computer monitor. A computer monitor is used to display images and texts. Most monitors have a casing, a wide screen on the front, and buttons to control how the screen displays the images and text and the obvious power-on-and-off button. Different monitors have other ports, which are core to the functioning of the monitor or used to extend the functionalities of the computer monitor.
Traditional monitors used the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) technology to work. CRT monitors were often large, bulky and occupied a lot of deskspace. (The use of past tense is intentional as CRT monitors have been hastily phased off)

New monitors are built using the LED (Light Emitting Diodes) technology or the more modern LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). LED and LCD screens are slim and often referred to as flat-panel displays.

Computer Keyboards
A keyboard is used to input instructions into a computer, and is often classified as a computer's input device. A keyboard contains all characters that can be recognized by a computer, including letters, numbers, and special characters. We use a keyboard to communicate with a computer through a process commonly known as typing.

Computer Keyboard Image - A QWERTY-Oriented Keyboard
Keyboards come in different sizes, colors and layouts; however, one of the most common layouts iis the QWERTY keyboard, derived from the letters following each other as shown below.
Other common layouts are QWERTZ, and AZERTY.
Keyboards are also of different types. There is the common computer keyboard used to type. There are also gaming keyboards with additional features that make gaming easy. Number keyboards contain only characters that are commonly used with arithmetics (Numbers, arithmetics signs)
Computer Mouse
A mouse is another common computer input device used to send instructions to a computer. It is also known as a pointing device. A mouse allows us to point on images on the screen, click on them, and drag them to any point on the screen.
A mouse can either be mechanical, optical, or laser. A mechanical mouse has a ball at the bottom, which rolls to move the pointer on the screen. An optical mouse uses light to detect and track the movement of the mouse. Modern optical mice can be used on any surface including a mouse pad, wood, and glass. Earlier versions of the optical mouse required a special pad to properly function. Modern technologies have also contributed to the development of laser-driven mice that are tolerant to more surfaces than the optical mouse.
A laser-based mouse uses an infrared laser diode instead of an optical LED (for optical mouse) to detect movement and direction. A laser mouse offers high sensitivity allowing for precise tracking of mouse movement. Depending on the features, you can classify a computer mouse in different ways.
Connector Type
There are different types of mouse connectors.
USB Mouse
A USB mouse uses a wire to connect the mouse to the computer through the standard USB port, located at the front or at the back of a computer. The USB wire helps power the mouse from the computer and send instructions from the mouse to the computer. The most common computer mouse has three main components to generate instructions; a left-click button, a right-click button, and a scrolling wheel.
Wired Mouse Image

Wireless Mouse
A wireless mouse, as the name suggests, does not connect to the computer through a wire or a cord. Wireless mice can use different technologies to connect to the computer, including Bluetooth or other radio frequencies (RF). A wireless mouse is more portable and can be used from a distance from the computer, a feature dependent on the signal strength between the mouse and the computer.
Wireless Mouse Image

What powers a wireless mouse?
As earlier discussed, USB and PS/2 mice are powered by the computer power through the connecting wire. But what powers a wireless mouse? A wireless mouse can either use one-time-use removable batteries (AA or AAA) or rechargeable batteries. The latter is a more modern feature where a mouse has a 5V charging port.
PS/2 Mouse
A PS/2 mouse uses the green PS/2 port usually located at the back of a computer. However, the PS/2 mouse has been phased out and replaced by the modern USB and Wireless mouse.

Trackball
A trackball can either be wireless or wired. Its primary feature is the presence of a 'ball' at the top or one of the sides (mostly to the left). The trackball is different from the mouse in terms of functionality and design. Although technically a trackball is a mouse it is often referred to as a 'trackball' to uniquely identify the device.

Trackballs have existed since around 1947 and have continued to evolve in design and functionality. One of the reasons trackballs have survived the test of time is their ergonomic characteristics.
Internal Parts
Computer Motherboard
If it was in the music band, the motherboard would be the lead vocalist. The main person who links the other singers and the instrument players.The motherboard brings all the other components together to form a complete computer. A motherboard houses other computer components such as the Central Processing Unit (CPU), USB connectors, various display and printer connectors, and hundreds, if not thousands, of electrical components such as transistors, capacitors, resistors, and chipsets.
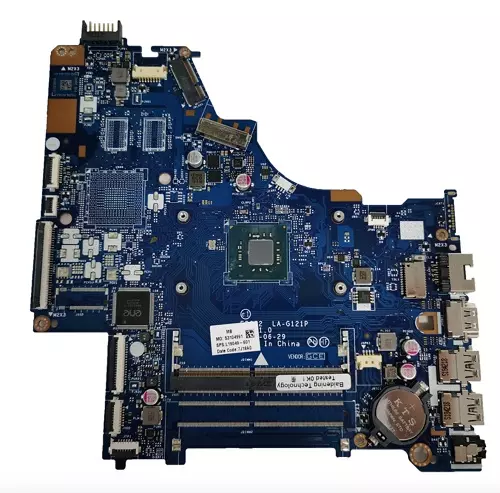

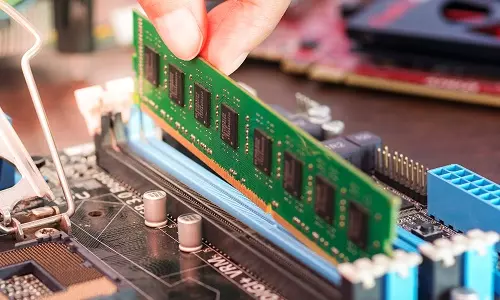
Motherboards come in different sizes depending on the intended functionalities, size of the computer case, and size of internal components. Motherboards have ports that can be accessed from the outside such as USB, Display, and Printer ports. In addition, there are ports and slots that can be accessed only by opening the case. Such slots include CPU and Random Access Memory (RAM).
Computer CPU (Central Processing Unit)
As the name suggests, the CPU is the unit tasked with processing instructions sent to the computer. Central does not translate to its position on the motherboard, rather its importance in the functionalities of a computer. Think of a section on the road where other roads meet. The CPU is the position on the road connecting all other roads. A better example, think of a CPU as the brain of the computer. Just like us humans, the brain translates signals. When you see something, the brain translates that image. In computers, when you click on something, the CPU translates that signal and responds according to a set of instructions.
Computer GPU (Graphical Processing Unit)
If you are a gamer, work with HD video editing, or intense graphical programs, the GPU is definitely your computer's closest cousin. Modern games have high-end visuals that modern CPUs cannot keep up with. With a GPU, your computer can render graphics, including those in 3D, and tackle creative production and artificial intelligence (AI) tasks with ease.
Computer RAM (Random Access Memory)
Random Access Memory is a temporary/volatile form of memory that stores data of active programs and processes. Due to its volatile nature, RAM data is usually erased once you close a program, close a process, or shutdown a computer.
Computer RAM Image
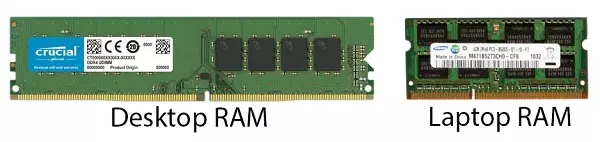
Why store data in the RAM?
Modern CPUs are tasked with executing at least one million instructions every second. RAM holds data so that it can be quickly reached by the CPU for execution.
RAM speed is measured in Megahertz (MHz). Further, evolution has seen different types of RAMs being produced with better functions, higher speeds, and greater sizes.
RAM is one of the devices that you can upgrade to improve your computer's performance for usual operations and even gaming. If a program you want to install has 8GB RAM as the minimum required and your computer has 4GB installed, do not panic! You can buy another 4GB RAM module and install it on your computer. For this operation, you will have to open your computer casing to access the empty RAM slots on the motherboard.
Computer Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or Solid State Drive (SSD)
You want to install a favorite program. You want to download a photo of your favorite celebrity to your computer. Well, the HDD and SSD, are devices used to store data in a computer. Unlike the RAM, HDD and SSD offer a more permanent, non-volatile, form of data storage. The HDD is a fairly older storage technology than the SSD. HDDs are way cheaper than SSD; however, they are slowly becoming more and more obsolete.
Both HDD and SSD's storage spaces are measured in terms of bytes.
The HDD consists of actual magnetic disks (or platters) that rotate at high speeds. A mechanical arm helps read and write data onto the platters. HDDs are of different shapes and physical sizes. Further, HDDs' rotating speeds are measured in revolutions per minute (RPM) , a contributing factor to their different write and read speeds, and therefore performance.
Optical Drivers
You might not have used these for a long time or even once since you got access to a computer. I can bet you have seen a computer without an optical drive. The data on CDs and DVDs can be accessed through a computer's optical drive. However, the use of CDs and DVDs to store music, videos, and other forms of data has consistently dropped, hence the less emphasis on optical drives are a feature on modern computers.
... Is that all?
Well, no. There are lots of other components that make up a computer that are attributed to the computer's performance and functionalities. Whereas this article might not cover all, our other articles are dedicated to diving deeper into the functioning of a computer and what happens behind the scenes, once you press the power on button on your computer.