Common RAM Failure Symptoms: What to Look For and What to Do
Which are the common signs of a failing/failed computer RAM? My RAM is failing, what can I do? Read on how to pinpoint a failed RAM and replace it.
What is RAM?
RAM, commonly known as Random Access Memory, is a hardware component typically found on the motherboard of devices. Its purpose is to act as an intermediary between a device's CPU and its storage device, be it an SSD or HDD. Unlike permanent storage, RAM is volatile in nature, meaning it temporarily stores data for active applications and processes.
RAM, which stands for Random Access Memory, is an essential hardware component found on the motherboard of various devices. It plays a crucial role in facilitating communication between a device's CPU and its storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disk drives (HDDs). Unlike permanent storage options (such as SSD/HDD), RAM is a temporary form of memory that stores data for currently active applications and processes. This dynamic nature of RAM enables efficient multitasking and quick access to frequently used data, resulting in smoother and more responsive user experiences.
RAM, being a hardware device, is susceptible to heat exposure, primarily generated by system components like the CPU and other electrical elements. Prolonged exposure to heat can contribute to the eventual failure of RAM over time. Additionally, power-related problems can also lead to RAM failure, such as sudden power loss during system operations. Power issues like power surges or faulty electrical components can even cause damage to the motherboard, including the RAM modules. It's worth noting that inferior quality or counterfeit RAM modules tend to deteriorate more quickly, resulting in faster failure compared to genuine RAM modules. Lastly, like any hardware component, RAM modules can experience natural wear and tear over time due to regular usage, leading to eventual failure.
A failed RAM can be characterized by various system occurrences. The most common occurrences are discussed below:
1. Black Screen during Computer Booting
While a faulty computer memory module may not prevent the computer system from booting, it can result in a black screen with no display output. Less-critical RAM failures might go undetected by the system, but some computers may emit a beeping sound or flash the CAPS LOCK key on the keyboard as indicators. However, if the computer does not exhibit any of these symptoms, it is likely that the RAM has not experienced a critical failure. Nevertheless, memory issues can still impact the system's graphics during the Power On Self Test (POST) phase, affecting the display and overall functionality of the computer during startup.
2. Random Restarts
An additional indication of RAM failure or impending failure is the occurrence of abrupt restarts without any clear cause, such as a system update or a program requiring a restart for installation or uninstallation. RAM plays a vital role in the functioning of a computer system, and if it fails to perform as expected, it can trigger an automatic reboot as an attempt to resolve the encountered error. Sudden restarts, particularly in the absence of any specific trigger, can often be attributed to RAM-related issues and should be investigated further to determine the root cause.
3. Frequent System Crashes (BSOD)
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a critical error screen that appears when a Windows operating system encounters a fatal system crash. When such an error occurs, a blue screen is displayed, notifying the user that "Windows needs to restart the device." The BSOD serves as an indication that the system has encountered a severe error from which it cannot recover, leading to the need for a system restart in order to resolve the issue. The purpose of the BSOD is to provide diagnostic information about the error, which can help in identifying the underlying cause of the crash and troubleshooting the problem effectively.

When a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) occurs, its duration can vary depending on the system settings and the severity of the error. In some cases, the BSOD may only flash briefly, making it difficult to read the notification, while in other cases, it may remain on the screen for a longer period, allowing the user to review the error message.
Following a BSOD, the system will indeed automatically restart as part of its attempt to resolve the underlying hardware or software issues that caused the crash. The restart is intended to initiate a fresh start and potentially recover from the encountered problem.
It's worth noting that faulty RAM can indeed be a common cause of frequent BSOD crashes. When the RAM is defective or experiencing issues, it can lead to instability in the system, resulting in recurring crashes and triggering the BSOD. In such cases, diagnosing and replacing the faulty RAM module(s) can help resolve the issue and prevent further BSOD crashes.
4. System Freezing or Locking Up
RAM plays a crucial role in providing memory space for the applications and programs running on a system. When the RAM fails or becomes faulty, it can lead to various symptoms, including frequent freezing and locking up of the system. These issues manifest as the computer becoming unresponsive, with programs crashing or not responding as expected.
In more severe cases, the screen may completely freeze, and basic inputs from the mouse or keyboard may not have any effect on the system. These critical system freezes often result in a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) crash, indicating a serious error that requires a system restart to address the issue.
When RAM fails, it can disrupt the normal functioning of the system's memory management, leading to these freezing and locking up symptoms. Diagnosing and resolving the RAM-related problem, such as replacing faulty modules, can help restore the system's stability and prevent further crashes and freezes.
5. Application Errors and Unexpected Behavior
Indeed, faulty RAM can lead to unexpected behavior in applications, often accompanied by memory-related notifications. These notifications can vary depending on the specific program or application being used. Memory-intensive applications such as games, graphic software, and audio-visual editing programs are particularly susceptible to exhibiting these behaviors when there are issues with the RAM.
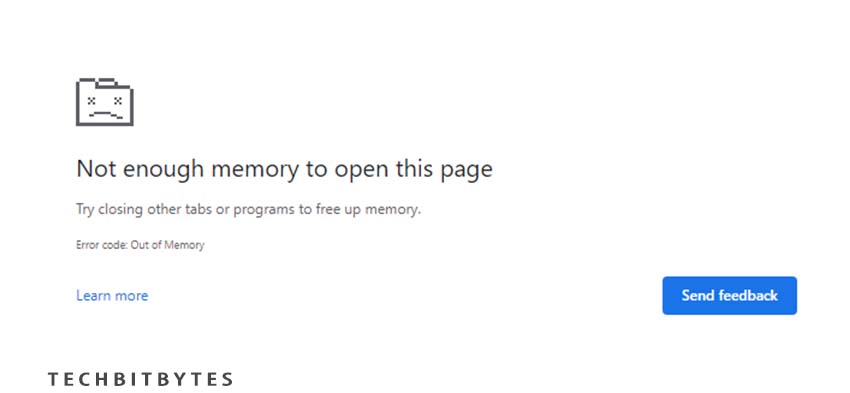
Users may encounter memory-related error messages while using such applications, indicating problems with memory allocation or insufficient available memory. These messages can range from notifications about low memory warnings to specific error codes related to memory access or allocation failures.
Additionally, during system booting, a notification may appear indicating a memory-related error message. This can occur when the installed RAM fails a memory test during the Power On Self Test (POST) phase of the boot process. The system recognizes the issue and alerts the user to the presence of faulty RAM.
When encountering these memory-related notifications and error messages, it is important to address the underlying RAM issue. Troubleshooting, running memory tests, or replacing faulty RAM modules can help resolve these problems and ensure proper system functionality.
6. Slow Performance and Increased Loading Times
In our article about RAM and its types, we emphasize the direct impact of RAM on the overall performance of a computer system. When RAM becomes faulty or fails, it can significantly hinder the system's performance, leading to various symptoms.
One of the noticeable effects of faulty RAM is a general slowdown of the computer system. This can manifest as a decrease in overall responsiveness and a sluggishness in executing tasks. Applications may take longer to load, and there may be noticeable delays when switching between different programs or tasks.
A key indicator of failing or failed RAM is the system's unresponsiveness or a significant reduction in its responsiveness. When RAM is not functioning properly, it can hinder the system's ability to handle and manage data effectively, resulting in slower performance and decreased responsiveness.
It's important to recognize that RAM plays a crucial role in providing fast and efficient access to data that is actively used by the computer. When RAM fails, the system has to rely more heavily on other forms of storage, such as hard drives, which are significantly slower in comparison. This reliance on slower storage mediums can lead to the observed slowdowns and decreased system performance.
A failing or failed RAM can have a detrimental impact on the performance of a computer system, causing general slowdowns, longer loading times for applications, delays when switching between tasks, and an overall unresponsive or slowed-down user experience.
Resolving RAM / Memory-Related Issues
If you have a single RAM module installed and encounter issues, it is likely that the installed RAM module itself is the culprit. However, when multiple RAM modules are installed, it becomes challenging to determine which one has failed. In such cases, a systematic testing process is required to identify the problematic module.
To identify the faulty RAM module, follow these steps:
Begin by removing all the RAM modules except for one, ensuring that the remaining module is properly seated in its slot.
Run the built-in memory tests available in the BIOS menu. These tests can help identify any errors or issues with the RAM module.
If the memory test passes without any errors, it indicates that the tested RAM module is likely functioning correctly.
Repeat this process with each RAM module, testing them individually to identify any faulty modules. Ensure to test each module in the same RAM slot to eliminate potential slot-related issues.
Note that in some cases, the RAM slot itself may be causing the problem, which is a critical motherboard issue. If you suspect a faulty RAM slot, you can try swapping the RAM module to another empty slot. If an empty slot is available, and the RAM functions properly in the new slot, you can continue using the system with the functional slot.
However, if there are no available empty slots or the issue persists, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a technician for further diagnosis and resolution of the problem.
When troubleshooting multiple RAM modules, you need to test each module individually using the built-in memory tests. Additionally, if a RAM slot is suspected to be the cause of the issue, swapping the RAM module to an empty slot can help identify any slot-related problems.
When a RAM module fails, the most common and effective solution is to replace it with a new one. Repairing a failed RAM module is generally not a viable option, as RAM modules are not designed to be repaired at the component level.
Fortunately, RAM modules are relatively affordable, and their prices can vary depending on the type and specifications. As of 2023, prices for RAM modules can range from $12 to $25, depending on factors such as capacity, speed, and generation (PC4, PC3L, PC3, etc.). These prices make it cost-effective to replace a failed RAM module rather than attempting repairs.
It's important to note that when replacing a faulty RAM module, it is crucial to ensure compatibility with the motherboard and other existing RAM modules. Checking the specifications and supported memory types of the motherboard is necessary when choosing the appropriate replacement module.