What is screen tearing? How do I fix it?
What are the main causes of screen tearing in gaming? A simple step-by-step guide on how to fix screen tearing for computer and console gaming.
Introduction
If you have watched a film on a monitor or played games on a gaming console or a personal computer (PC), we can bet you have experienced, at least once, screen tearing. You might ask; What is screen tearing? Is it only experienced while gaming? Can it be fixed? In this article, we will try to address the concept of screen tearing in relation to display resolution and refresh rate.
Two main components of a computer are responsible for generating and displaying videos; a Graphical Processing Unit (GPU) or a Central Processing Unit (CPU) and a Display, also known as a monitor, which can be a computer monitor or a TV. High-end computers and gaming consoles have dedicated GPUs responsible for graphical performance while standard computers task graphical operations to their CPU since the GPU is integrated into it.
Screen tearing is where an image on your monitor appears distorted either for a brief period or continuously. Screen tearing is mainly caused by:
A PC's or gaming console's GPU/CPU
When prolonged, screen tearing can strain your eyes due to the visual distraction caused. The image below shows a screen-tearing occurrence in a game.
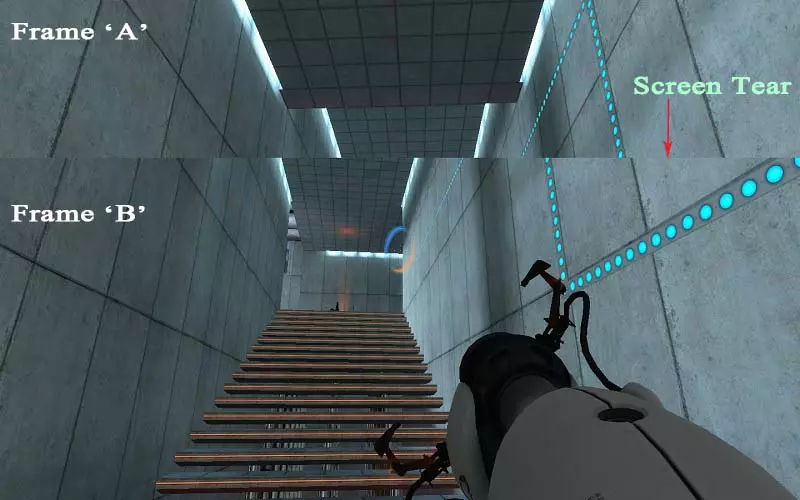
While playing a video (film or a game) it is important to note that each second has tens (or hundreds in the latest display technologies) of still images being displayed across your monitor. The images are displayed so fast that our minds perceive them as moving images or videos. These still images are also known as Frames. The number of frames supported by a monitor is identified as FPS (Frames per Second). Today, most common monitors have a 60 FPS rating.
How Do I Find my Display's Refresh Rate / FPS?
If you do not see the FPS rating on your monitor, check the frequency, which can be marked as 60 Hz. While 60 hertz indicates the refresh rate (how many images are drawn on a monitor every second), FPS indicates the number of frames drawn on the screen every second. Therefore, you can see a relation between Hz and FPS and that is the reason why they are at times used interchangeably. Thereby, we can use both 60Hz and 60 FPS to indicate that a monitor has a refresh rate of 60.
Your GPU or CPU is responsible for generating the frames and sending them out to the monitor for display. Both devices, GPU and monitor, have Hz or FPS values that indicate the number of images processed every second.
What Causes Screen Tearing?
So, why does screen tearing occur?
As you have read above, two components contribute to screen tearing; that which is responsible for generating the frame/images - either a GPU or CPU - and that which is responsible for displaying them - the monitor (or TV). When the computer-generated frame rates (FPS) fail to properly match the FPS of the outputting monitor, highly likely you will experience a scream tear. The bigger the disparity between the two frame rates, the bigger the size and scale of the screen tear.
For instance, an out-of-synchronization display can occur if your computer's GPU is generating frames between 30 FPS and 60 FPS for a triple-A (AAA) game while the connected monitor is rated 60 FPS. Further, connecting an overrated GPU or using a GPU beyond its baseline standard capabilities can cause screen tearing if the monitor does not match or exceed the standards. For instance, setting FPS on a GPU at 120 Hz while the output monitor is rated at 60 Hz.
While a monitor can support 60Hz, your gaming console can output frames unevenly - meaning, it can output 55 FPS one second, 40 FPS the next, 30 FPS the next, 59 FPS the next second, and so on. These variations are attributed to video lag or screen tearing - where there are clear cuts across the screen that show different times of the same image as shown below. {See Section on VRR in DisplayPort vs HDMI}
Onboard Graphic Processing Units (GPU) have accompanying RAM (See normal RAM on Computers) that offers the same service as computer RAM. Sufficient GPU RAM or GPU memory help improve graphic performance more so when working with graphic-intensive applications such as AAA games or demanding video editing software applications. When the GPU memory is insufficient, you will notice screen tears, which become worse as the memory deteriorates.
How to Fix Screen Tearing
Now that you understand what screen tearing is, let's explore ways that you can avoid them or even fix them if they happen to occur.
1. Match Hardware Requirements
As we explained earlier, the biggest contributor to screen tearing is out-of-sync FPS values for GPU/CPU and monitor. Therefore, one way to avoid instances of screen tearing is to ensure that the FPS rate on your computer or gaming console
For instance, if your PC's GPU/CPU is rated 60 FPS, ensure that your monitor also has a 60 FPS.
2. Adjust Refresh Rate and Display Resolution
Ensure that your GPU's FPS matches the computer (monitor) refresh rate and display settings. Further, the output GPU resolution should match the display resolution for your monitor.
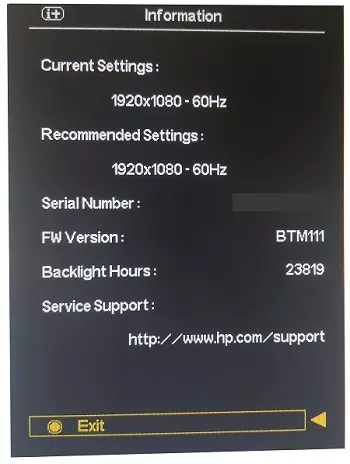
It is important to check the recommended display resolution and refresh rate of your monitor and find the settings in your GPU resolution or computer resolution settings. Depending on your display, go to the options menu on your display (monitor) and search the display information cluster.
Below is the display information cluster for a HP Monitor:
On your computer, go to display settings and search for the resolution that matches the display resolution. In some cases, you'll find a recommended hint on one of the listed display resolutions.
Here is a guide on adjusting display resolution and refresh rate on a Windows 10 PC.
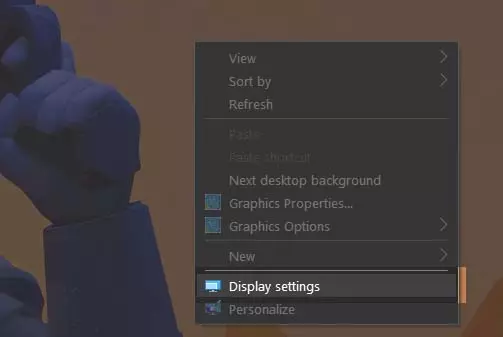
Step 1: Right click on an empty area on your desktop. You should get the dialogue box shown below. Click on Display settings.
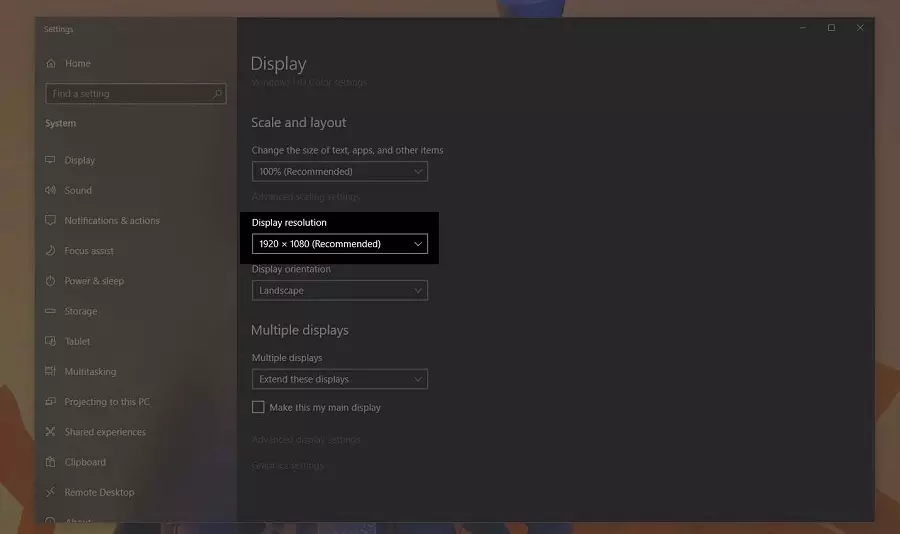
Step 2: In the next Display window, find the Display resolution section and click on the drop-down arrow.
Step 3: Trace the display resolution that matches your display's recommended resolution.
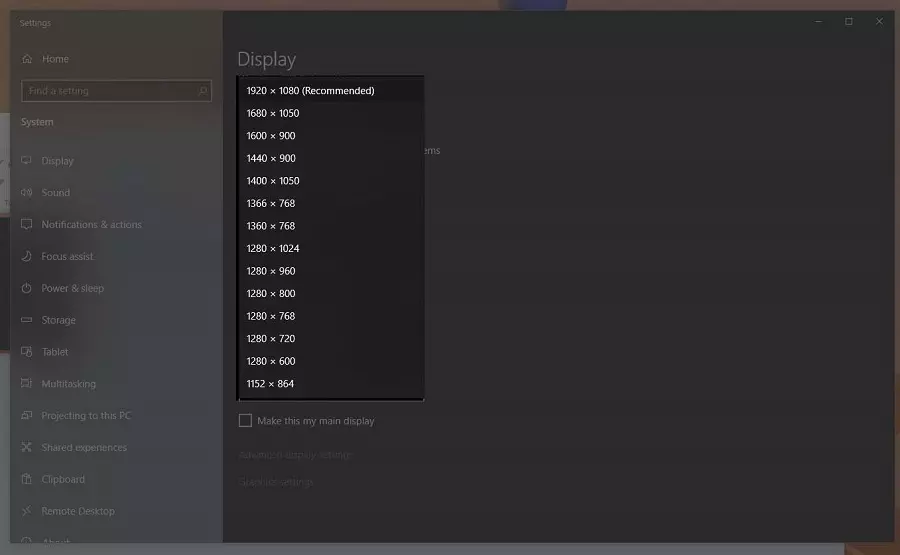
Step 4: To adjust the refresh rate, search the Advanced display settings at the bottom of the display window. Find the Refresh rate section and click the drop-down arrow
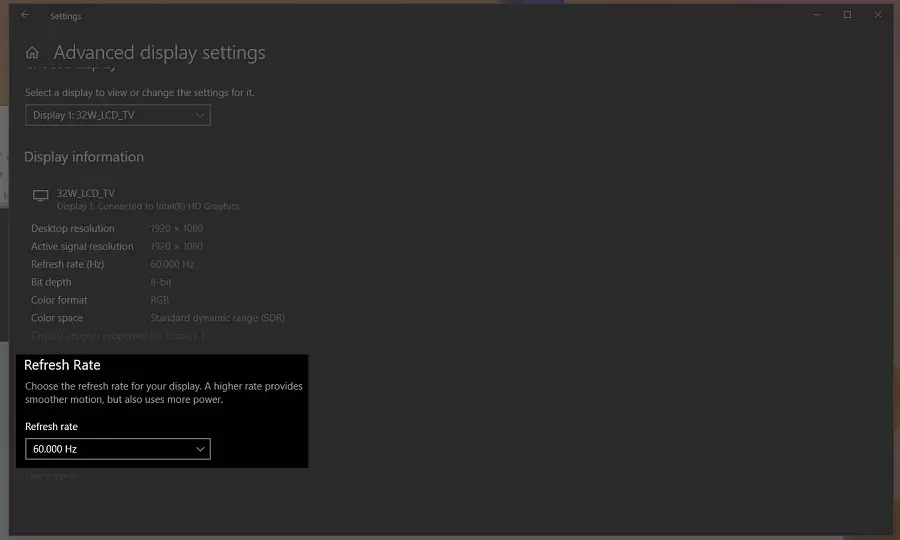
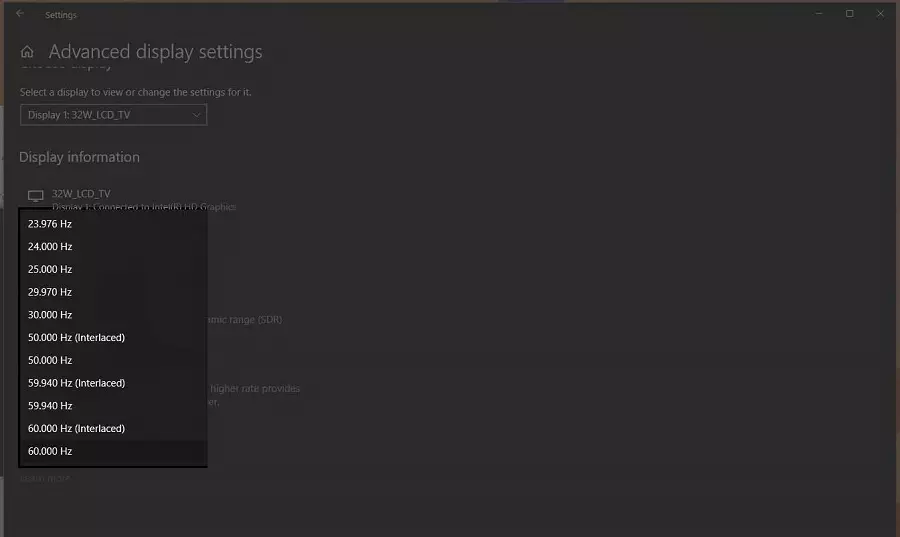
Step 5: Trace the refresh rate matches your display's recommended resolution.
3. Check Graphic Drivers and Updates
If you installed GPU hardware and suddenly you experience screen tearing when gaming, or watching a film, check the drivers of the new hardware against the latest updates. Ensure that the latest GPU drivers are installed and configured appropriately. Visit the GPU manufacturer's website to see if any updates have been released and read about any issues discovered with the hardware in terms of performance.
Whereas computer OS and Software updates are necessary, incompatibility issues between new updates and existing hardware can compromise normal performance and operations. If you experience screen tearing after software, graphic drivers, or system updates, check if any incompatibility information has been flagged. You can eliminate the screen tearing by rolling back any updates or re-installing an older version of the application if rolling back is not an option.
4. Turn AMD FreeSync Feature on AMD GPU On/Off
AMD FreeSync is a popular FPS adjustment function that uses Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) technology to prevent screen tearing and ghosting. VRR technology attempts to match the frame rate of the computer-generated images to that of the monitor's refresh rate through adaptive synchronization. You can enable FreeSync through AMD's control settings
Turning on VRR may help prevent screen tearing. However, if you experience screen tearing when AMD's FreeSync feature is turned on, disabling it may solve the problem.
5. Turn NVIDIA G-SYNC on NVIDIA GPU On/Off
Just like AMD FreeSync, NVIDIA G-SYNC uses adaptive synchronization to match the GPU FPS to the display's FPS to prevent screen tearing and ghosting. NVIDIA G-SYNC feature can be turned on from the GPU control panel to prevent screen tearing.
At times, the VRR feature can create compatibility issues between the GPU/CPU and the display. Therefore, if screen tearing occurs when VRR is turned on, turning it off (disabling) may resolve the issue.






