How to Fix a Freezing Computer: 9 Common Causes and Solutions
Are you experiencing a freezing computer? This can be a frustrating problem, but there are a number of reasons why it might be happening. In this article, we'll discuss 9 common reasons why your computer might be freezing, and what you can do to fix the problem.
Experiencing the thrill of completing your final task on your work PC before the weekend, dominating the last lap in your beloved PC racing game with the pursuing car hot on your tail, or being captivated by an epic movie scene on your PC can be incredibly enjoyable. However, in these moments of excitement, you may encounter an unwelcome interruption – your PC freezing. The computer system intermittently halts responsiveness to keyboard and mouse inputs, the display freezes, and applications stubbornly display the "Not Responding" notification. In this article, we will look into the 9 most common reasons causing your PC to freeze and become unresponsive. We'll provide effective solutions to safeguard your PC from the frustrating episodes of unresponsiveness.
9 Reasons Why Computer Keeps Freezing
1. Insufficient Memory on your PC
RAM (Random Access Memory) plays a crucial role as a core internal component of a PC. It serves as volatile memory, facilitating communication between the computer's CPU and storage; SSD and HDD. However, when your PC falls short on memory to efficiently handle the system process and applications, it can lead to a host of frustrating issues, the most common being freezing and slowdowns. Insufficient RAM size on your PC it is a common cause of frequent computer freezes and noticeable unresponsiveness.
2. Many Background Processes and Programs Running
Every open program uses system resources like RAM, CPU Cache, and I/O processes. Therefore, having too many programs open can lead to freezing and unresponsiveness. In some cases, a single program can become unresponsive, freezing the entire computer in the process. While modern PCs have strong resource management, some systems may still experience unresponsiveness when many programs are running. Additionally, resource-intensive background processes can cause the system to freeze and slow down.
3. Overheating
If your PC runs smoothly during startup but starts to slow down after normal operations, it's essential to consider the possibility of overheating. Computers components, more so the CPU, GPU, and I/O chip, generate heat during their regular operations. Additionally, other electrical components within the integrated circuit (IC) also contribute to the heat generation. When temperatures rise to extremely high levels, it can adversely affect normal operations, leading to system slowdowns and freezing.
It's crucial to be aware that both the CPU and GPU have maximum temperature limits. For instance, the Intel® Core™ i9-9980XE Extreme Edition Processor has a Junction Temperature (TJunction) of 82°C (~180°F). Junction Temperature is the maximum temperature allowed at the processor die. When the CPU temperature nears this limit, the computer system employs protective measures and abruptly shut down to prevent damage to its components. In these extreme cases, in addition to slowed performance, you also experience sudden shutdowns with or without the blue screen of death (BSOD).
4. Malware and Viruses
Malware disrupts the smooth functioning of a PC by diverting system resources, including memory, that should be reserved for legitimate processes. The impact of malware on a computer system can vary based on its payload and design. It may lead to slowed performance, system freezes, unresponsiveness, or even complete shutdown. Malware can also be designed to turn a PC into a part of a DDOS botnet or execute resource-intensive background processes, deliberately consuming PC resources and causing unresponsiveness even during less operations, such as during startup. The consequences of malware infestation can be severe, necessitating robust security measures to safeguard your PC from such threats.
5. Faulty Peripheral Devices (Failed / Failing Hardware)
A PC comprises various internal and external hardware components, each playing a crucial role in its overall performance. If any of the internal components, such as the HDD, SSD, GPU, or RAM, fail, it can result in instability, slowdowns, and even freezing of the system. Additionally, faulty external hardware like keyboards and external storage devices (e.g., HDDs and flash drives) can also cause a computer to freeze and become unresponsive.
It's essential to recognize that hardware-induced slowdowns can stem not only from faulty components but also from incompatible hardware. When incompatible hardware is installed, it can create conflicts at both the software and hardware levels, leading to system freezes and unresponsiveness. In severe cases of incompatibility, a PC may shut down unexpectedly or fail to start entirely.
6. Outdated or Corrupt Drivers
System drivers play a crucial role in enabling hardware communication with the operating system. Every hardware component in a computer requires specific drivers to ensure it is recognized by the OS and functions as intended. When hardware drivers are missing, the associated device may not be recognized and entirely fail to function or may operate erratically. Similarly, outdated or corrupted drivers can lead to system instability, resulting in freezing and unresponsiveness.
7. Missing or Corrupt System Files
System stability heavily relies on critical system files that store vital information about the computer's processes. When these files are missing or corrupted, the system becomes susceptible to frequent freezes and sudden shutdowns, often accompanied by the notorious "blue screen of death" (BSOD). System files can be deleted or corrupted due to several factors including:
Software Issues: Bugs resulting from programming errors in software can inadvertently delete or corrupt system files. Additionally, errors during software installations, updates, or uninstallations can lead to issues with crucial system files.
Malware and Viruses: Malicious software is intentionally designed to target and manipulate system files, causing deletion or corruption and disrupting system stability.
Interrupted System Updates: Incomplete system updates, particularly on Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 7 PCs, can leave system files in an incomplete state. Installing incompatible updates can also create conflicts and lead to system file corruption.
Failed Storage Devices: Storage devices like SSDs and HDDs with bad sectors can experience data corruption, including system files, resulting in system instability.
Conflicts with Third-Party Software: Certain third-party applications may inadvertently modify system files, leading to corruption and subsequent issues.
Unexpected Power Loss or Improper Shutdown: Abrupt power loss or improper shutdown can interrupt file write operations to system files, causing corruption and compromising system stability.
Human Error: Accidental deletion of system files can occur when users with the necessary privileges manually modify system settings.
8. Overclocking
Overclocking the CPU and GPU can offer a tempting promise of heightened system performance and speeds. Overclocking these components pushes them beyond their default or manufacturer-recommended settings in an attempt to unlock a system's full potential.
However, it's essential to be aware of the potential consequences that can arise from pushing these components beyond their stable limits. These include:
Increased heat generation within the system - the intensified workload puts additional stress on the CPU and GPU, leading to elevated temperatures. Without proper cooling solutions, this can result in system instability and possible sudden shutdowns as the components strive to protect themselves from damage.
Impacts power and voltage management within the system. Higher clock speeds require increased voltage levels. Therefore the system faces the risk of electrical instabilities and voltage-related issues. These instabilities can affect the overall reliability of the system, leading to crashes and freezes.
Can introduce timing errors in the communication between different components of the system, which can cause data corruption resulting in system crashes and disruptions to normal operations.
Compatibility issues: Some hardware and software applications are optimized to function optimally with default CPU and GPU settings. Overclocking can lead to incompatibility issues, causing system instability and crashes due to the mismatched operating standards.
Accelerated wear and tear: System components experience increased stress caused by higher temperatures, speeds, and voltages. This can result in premature component failure and further instability.
9. Insufficient Disk Space
System processes continuously write data to the disk, especially the C drive, which is typically the default OS installation disk. However, when the disk reaches its storage capacity, especially the virtual disk used for temporary files, it can lead to significant performance issues, as the system struggles to write and manage data effectively. This causes frequent freezes, and unresponsiveness, as programs to take longer to load or respond.
How to Fix Computer Freezes
Here are some common fixes if your computer keeps freezing and shutting down abruptly.
1. Check for Malware and Viruses
It is advisable to run a reputable antivirus or anti-malware software. If you suspect your PC is infected hence the slowed performance, update your antivirus or anti-malware software program and run scans to detect and remove any malicious programs or applications present on the system. Additionally, to ensure maximum effectiveness, keep your antivirus or anti-malware application updated with the latest signatures and ensure it is actively running, not disabled. By following these precautions, you can effectively safeguard your system from malware-induced freezes and ensure a smooth and responsive computing experience.
2. Free Up Disk Space in the C: Drive
If your C drive, or the drive containing the OS files is full, or nearly full, begin by creating additional space on the C drive by moving files to another drive with available space or deleting unnecessary files and applications.
Regularly assess your files and applications, identifying those that you no longer need or use. By deleting these unnecessary files, you can create additional space on your C drive, preventing performance slowdowns and potential system freezes. Moreover, consider transferring large files or data that are infrequently accessed to an external drive or secondary storage device. This strategy can help optimize the available space on your C drive, ensuring that it operates efficiently and avoiding potential issues related to low disk space.
3. Update All Device Drivers
Device manufacturers typically implement mechanisms to ensure that their devices' drivers are kept up-to-date. Many devices will trigger automatic checks for driver updates from the manufacturer's repository and either download them automatically or notify users of available updates. Additionally, manufacturers like Intel often provide dedicated applications that monitor and facilitate updates for their components in the computer, such as the CPU.
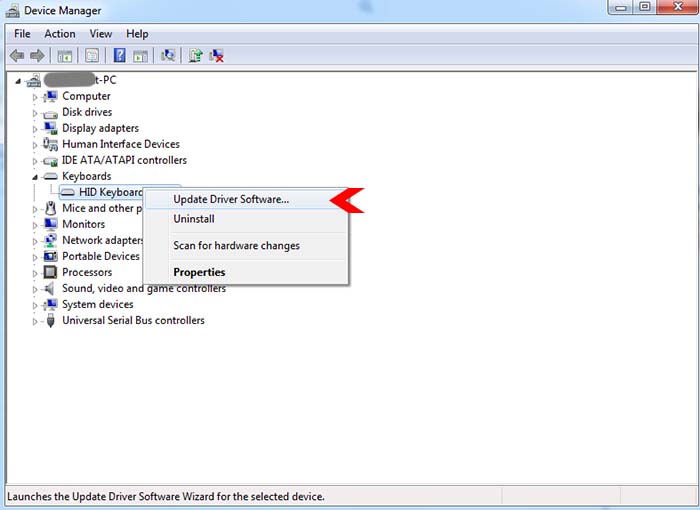
Further, as a user, you can manually check for device updates by accessing the Device Manager on your PC. Once in the Device Manager, locate the specified device, such as Keyboard click on it to, access its driver, right-click on the driver, and select the 'Update driver' option. Moreover, updating the Windows operating system can also trigger automatic updates for certain drivers, streamlining the process further. By employing these methods, you can ensure that your device drivers are regularly updated on your PC, thereby maximizing its performance and addressing potential compatibility issues, which can lead to the PC becoming unresponsive.
4. Scan and Check the System Files
Windows provides a built-in tool called "sfc /scannow" that allows users to scan the entire file system for missing or corrupted system files. To access this tool:
Open the Command Prompt in administrator mode by right-clicking on the CMD application and selecting "Run as administrator."
In the Command Prompt window, type "sfc /scannow" and press Enter.
Once you execute the command, Windows will initiate the system file scan, attempting to identify and fix any issues related to missing or corrupt system files. This built-in tool can help to restore the integrity of your Windows system and resolve potential problems that may lead to freezing or system instability.
5. Troubleshoot Faulty or Incompatible Hardware
If your PC experiences freezing after installing a new hardware component, such as RAM, SSD, HDD, or external devices like mouse, keyboard, printer, storage devices, or camera, it is possible that the added device has failed or is incompatible with your current system. To troubleshoot the issue:
Remove the device: Try removing the newly added hardware component or external device and check if the unresponsiveness still persists. If the freezing is resolved, it indicates a compatibility issue with the device.
Check compatibility: Review the compatibility information of the device to ensure it is compatible with your PC's specifications and operating system.
Verify drivers: Make sure all drivers for the device are properly installed. You can check the manufacturer's website for the latest drivers or use Windows Update to ensure you have the correct drivers.
Test in another PC: To rule out the possibility of a faulty device, install it in another PC and see if the freezing issue persists.
Seek professional diagnosis: If the freezing problem persists even after checking compatibility, drivers, and trying the device in another PC, consider taking the device to a PC repair shop for a comprehensive diagnosis.
By following these steps, you can pinpoint the cause of the freezing issue and take appropriate measures to resolve it, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted PC performance.
6. Check Application Against System Requirements
Before installing any application, it is essential to review the list of system requirements provided by the vendor. These requirements outline the minimum hardware and software specifications necessary for the application to function optimally. If you experience freezing or unresponsiveness on your PC after installing a specific application, it is advisable to check the application's system requirements.
You can find the minimum system requirements either on the vendor's website or in the documentation that comes with the installation file or manual. By verifying that your PC meets these requirements before installation, you can prevent issues such as insufficient memory or hardware incompatibility.
7. Check for Clogged Air Vents and Fans
Dust and debris can accumulate in a PC's air vents and fans, impeding the crucial circulation of air necessary for proper thermoregulation. If your PC operates smoothly for a while before becoming unresponsive, it may be a sign of elevated temperatures caused by failed fans or blocked vents. To address this issue, follow these steps:
Clear blockages: Check for any obstructions in the fans, vents, and the heatsinks, and ensure they are free from dust and debris. Cleaning these areas will help restore proper airflow and prevent overheating.
Fan maintenance: Ensure that all fans are functioning smoothly. If any fans are not working, consider replacing them to maintain proper cooling.
Check thermal pastes: If your PC has provisions for thermal pastes in the CPU and GPU contact points, inspect them to ensure they are in good condition. Reapply thermal paste if necessary to improve heat transfer and cooling efficiency.
Monitor temperatures: Install applications that allow you to monitor CPU and GPU temperatures. This will help you keep track of their heat levels and ensure they remain within safe limits during operation.
By taking these steps, you can enhance your PC's cooling efficiency and prevent overheating-related issues, such as freezing and unresponsiveness.
8. Cancel or Lower Overclocking values
Overclocking, which involves pushing the CPU and GPU beyond their default limits, as discussed earlier, can lead to various issues. If you experience freezing and slowdowns after overclocking your system, it is likely that the overclocking is the cause of these problems. To solve this:
Lower overclocking parameters: Reduce the overclocking parameters of the CPU and GPU towards their default settings. This can help stabilize the system and alleviate freezing and slow down issues.
Monitor performance: As you lower the overclocking parameters, closely monitor the performance of your PC. Keep an eye on temperatures and system stability to ensure that the adjustments are effective in resolving the issues.
Remove overclocking: In some cases, it may be necessary to remove all overclocking metrics from the CPU and GPU and revert them to the manufacturer-set defaults. This can be a safe approach to resolve system freezing and avoid potential damage caused by excessive overclocking.
By taking these measures, you can troubleshoot the freezing and slowdown issues attributed to overclocking, ensuring your system operates within safe limits and maintains stability. It is essential to strike a balance between performance enhancement and system stability when considering overclocking, and adjusting settings accordingly can help you achieve the desired results while safeguarding your PC's overall health.
9. Reduce Startup Programs
Certain PCs may experience freezing issues during startup because of the multitude of programs that automatically launch when the operating system loads. If your PC is encountering this problem, consider taking the following steps to resolve it:
Remove non-essential program from auto-start: Review the list of programs set to launch during startup and identify any non-essential applications. Disable or remove these programs from auto-start to reduce the workload during startup.
Change start triggers: For some programs, you can modify their start trigger from "On System Start" to "Manual." This change ensures that these programs will not automatically launch during startup but will still be available when needed through manual action.
By implementing these adjustments, you can streamline the startup process and reduce the strain on your PC's resources, ultimately mitigating freezing issues during boot-up. Prioritizing essential programs and minimizing the number of automatic startups will lead to a smoother and more responsive startup experience for your PC.